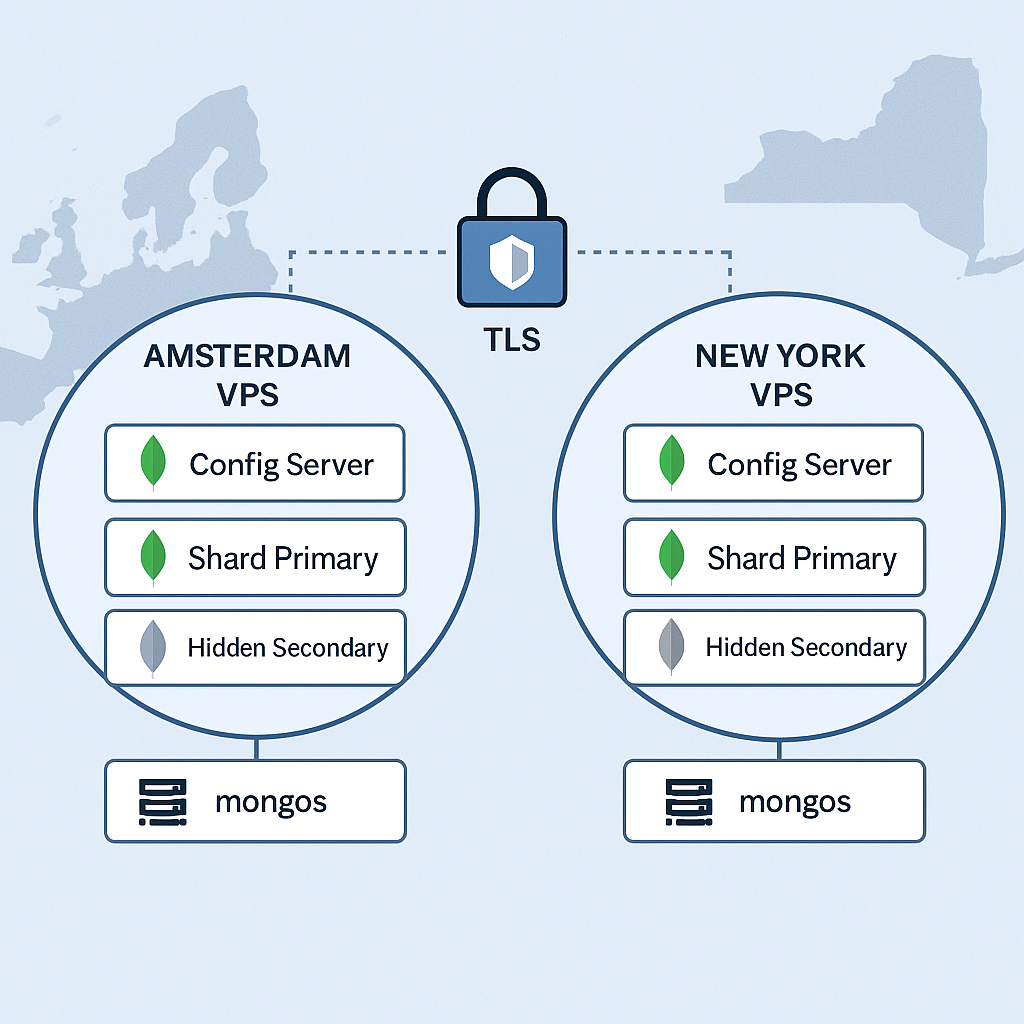
Building a geo-distributed MongoDB 7 cluster across continents requires careful planning for data locality, fault tolerance, and security. This comprehensive tutorial demonstrates how to deploy a production-ready geo-sharded MongoDB cluster spanning Amsterdam VPS and New York VPS instances, implementing zone sharding for optimal data placement, Config Server Replica Sets (CSRS) for metadata management, hidden secondaries for backup operations, and TLS encryption for secure communications.
This architecture ensures your MongoDB deployment can handle global traffic patterns while maintaining data sovereignty and providing disaster recovery capabilities across two strategic data centers.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with this deployment, ensure you have:
- 6 VPS instances: 3 in Amsterdam and 3 in New York (minimum 4GB RAM, 2 vCPUs each)
- Ubuntu 24.04 LTS installed on all instances
- Root access to all VPS instances
- MongoDB 7.0 Community/Enterprise knowledge
- SSL certificates or ability to generate self-signed certificates
- Network connectivity between all instances (ports 27017-27019)
- DNS resolution configured for all hostnames
Our deployment will use the following architecture:
- Amsterdam Zone: 1 Config Server, 1 Shard Primary, 1 Hidden Secondary
- New York Zone: 1 Config Server, 1 Shard Primary, 1 Hidden Secondary
- mongos routers: Deployed on application servers in both regions
Step 1: Install MongoDB 7 on All Instances
First, install MongoDB 7.0 on all six VPS instances. Execute these commands on each server:
# Import MongoDB public GPG key
curl -fsSL https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-7.0.asc | \
sudo gpg -o /usr/share/keyrings/mongodb-server-7.0.gpg \
--dearmor
# Add MongoDB repository
echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/mongodb-server-7.0.gpg ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0 multiverse" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-7.0.list
# Update package index and install MongoDB
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y mongodb-org
# Start and enable MongoDB service
sudo systemctl start mongod
sudo systemctl enable mongodVerify the installation on each server:
mongod --version
# Should output MongoDB 7.0.xStep 2: Generate TLS Certificates
For production security, we’ll generate SSL certificates for encrypted communications between cluster members:
# Create certificate directory
sudo mkdir -p /opt/mongodb/ssl
cd /opt/mongodb/ssl
# Generate CA private key
sudo openssl genrsa -out ca-key.pem 4096
# Generate CA certificate
sudo openssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -key ca-key.pem -out ca-cert.pem \
-subj "/C=US/ST=State/L=City/O=Organization/CN=MongoDB-CA"
# Generate server private key
sudo openssl genrsa -out server-key.pem 4096
# Generate server certificate signing request
sudo openssl req -new -key server-key.pem -out server-csr.pem \
-subj "/C=US/ST=State/L=City/O=Organization/CN=mongodb-server"
# Generate server certificate
sudo openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in server-csr.pem \
-CA ca-cert.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial \
-out server-cert.pem
# Combine server certificate and key
sudo cat server-cert.pem server-key.pem > server.pem
# Set proper permissions
sudo chown mongodb:mongodb /opt/mongodb/ssl/*
sudo chmod 600 /opt/mongodb/ssl/*Important: Copy the generated certificates to all cluster members and update the CN field with actual hostnames for production deployments.
Step 3: Configure Config Server Replica Set (CSRS)
Configure the Config Server Replica Set across both regions. On the Amsterdam config server (config-ams.example.com):
# /etc/mongod.conf
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
logAppend: true
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongodb
journal:
enabled: true
processManagement:
fork: true
pidFilePath: /var/run/mongodb/mongod.pid
net:
port: 27019
bindIp: 0.0.0.0
tls:
mode: requireTLS
certificateKeyFile: /opt/mongodb/ssl/server.pem
CAFile: /opt/mongodb/ssl/ca-cert.pem
sharding:
clusterRole: configsvr
replication:
replSetName: configReplSetApply similar configuration on New York config server (config-nyc.example.com), then start the config servers:
# Restart MongoDB with new configuration
sudo systemctl restart mongod
# Connect to Amsterdam config server and initiate replica set
mongosh --host config-ams.example.com:27019 --tls \
--tlsCertificateKeyFile /opt/mongodb/ssl/server.pem \
--tlsCAFile /opt/mongodb/ssl/ca-cert.pemInitialize the Config Server Replica Set:
rs.initiate({
_id: "configReplSet",
configsvr: true,
members: [
{ _id: 0, host: "config-ams.example.com:27019" },
{ _id: 1, host: "config-nyc.example.com:27019" },
{ _id: 2, host: "config-backup.example.com:27019", arbiterOnly: true }
]
});Step 4: Deploy Geo-Distributed Shards
Configure shard replica sets with zone awareness. For the Amsterdam shard primary:
# /etc/mongod.conf for Amsterdam shard
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
logAppend: true
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongodb
journal:
enabled: true
processManagement:
fork: true
pidFilePath: /var/run/mongodb/mongod.pid
net:
port: 27018
bindIp: 0.0.0.0
tls:
mode: requireTLS
certificateKeyFile: /opt/mongodb/ssl/server.pem
CAFile: /opt/mongodb/ssl/ca-cert.pem
sharding:
clusterRole: shardsvr
replication:
replSetName: shard01Initialize the shard replica set with zone tags:
rs.initiate({
_id: "shard01",
members: [
{
_id: 0,
host: "shard01-ams.example.com:27018",
tags: { "zone": "amsterdam", "region": "europe" }
},
{
_id: 1,
host: "shard01-nyc.example.com:27018",
tags: { "zone": "newyork", "region": "america" }
},
{
_id: 2,
host: "shard01-hidden.example.com:27018",
hidden: true,
priority: 0,
tags: { "zone": "backup", "region": "hidden" }
}
],
settings: {
getLastErrorModes: {
"multiZone": { "zone": 2 },
"multiRegion": { "region": 2 }
}
}
});Step 5: Configure mongos Routers
Deploy mongos instances in both regions for optimal routing:
# /etc/mongos.conf
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/log/mongodb/mongos.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
pidFilePath: /var/run/mongodb/mongos.pid
net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 0.0.0.0
tls:
mode: requireTLS
certificateKeyFile: /opt/mongodb/ssl/server.pem
CAFile: /opt/mongodb/ssl/ca-cert.pem
sharding:
configDB: configReplSet/config-ams.example.com:27019,config-nyc.example.com:27019Start mongos and add shards to the cluster:
# Start mongos router
mongos --config /etc/mongos.conf
# Connect to mongos and add shards
mongosh --host mongos-ams.example.com:27017 --tls \
--tlsCertificateKeyFile /opt/mongodb/ssl/server.pem \
--tlsCAFile /opt/mongodb/ssl/ca-cert.pem// Add shards to the cluster
sh.addShard("shard01/shard01-ams.example.com:27018,shard01-nyc.example.com:27018");
sh.addShard("shard02/shard02-ams.example.com:27018,shard02-nyc.example.com:27018");
// Configure zone sharding
sh.addShardTag("shard01", "amsterdam");
sh.addShardTag("shard02", "newyork");Step 6: Implement Zone Sharding
Configure zone-based sharding for optimal data locality:
// Enable sharding for your database
sh.enableSharding("myapp");
// Create sharded collection with zone-based shard key
sh.shardCollection("myapp.users", { "region": 1, "userId": 1 });
// Define zones for data placement
sh.addTagRange(
"myapp.users",
{ "region": "EU", "userId": MinKey },
{ "region": "EU", "userId": MaxKey },
"amsterdam"
);
sh.addTagRange(
"myapp.users",
{ "region": "US", "userId": MinKey },
{ "region": "US", "userId": MaxKey },
"newyork"
);Best Practices
Implement these critical optimizations for production deployments:
- Monitoring: Deploy comprehensive observability with MongoDB Compass, Grafana dashboards, and custom alerting for replication lag, chunk balancing, and connection pools.
- Backup Strategy: Configure hidden secondaries for consistent backups without impacting primary performance, implementing point-in-time recovery with oplog archiving.
- Connection Pooling: Implement proper connection pooling in your application drivers to handle geographic latency and connection management efficiently.
- Write Concerns: Use appropriate write concerns like
{ w: "multiZone", j: true }to ensure data durability across geographic boundaries. - Read Preferences: Configure read preferences for optimal performance, using
nearestfor geographically-aware reads andsecondaryPreferredfor analytics workloads.
Security Considerations:
- Enable authentication with SCRAM-SHA-256 or x.509 certificates
- Configure IP whitelisting and firewall rules
- Implement regular security auditing and access reviews
- Use encrypted storage-at-rest for sensitive data compliance
Conclusion
You’ve successfully deployed a production-ready geo-sharded MongoDB 7 cluster across Amsterdam and New York VPS instances with advanced features including zone sharding, Config Server Replica Sets, hidden secondaries for backups, and TLS encryption. This architecture provides excellent data locality, fault tolerance, and scalability for global applications.
The implementation supports compliance requirements for data residency while maintaining optimal performance through intelligent data placement and geographic routing. For enhanced reliability, consider exploring our guides on active-active VPS architectures and comprehensive monitoring solutions.
Ready to deploy your MongoDB cluster? Onidel’s Amsterdam VPS and New York VPS offer high-performance EPYC Milan processors, NVMe storage with triple replication, and advanced networking features perfect for distributed database deployments.